Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar, an essential medium in microbiology, unveils a captivating narrative that delves into its composition, applications, and significance in research and industry.
This versatile agar, composed of mannitol, sodium chloride, and peptone, plays a crucial role in isolating and identifying Bacillus subtilis, a bacterium with remarkable industrial and environmental relevance.
Introduction to Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar
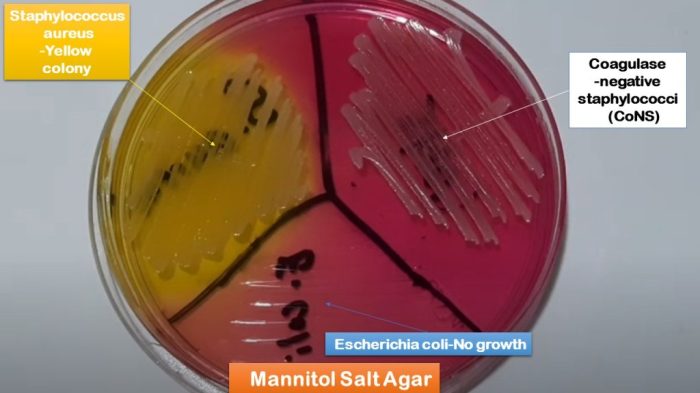
Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar (BSMA) is a selective and differential medium specifically designed for the isolation and identification of Bacillus subtilisand related species. It is widely used in microbiology and diagnostic testing due to its ability to differentiate B. subtilisfrom other bacteria based on their ability to ferment mannitol and tolerate high salt concentrations.
Uses of Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar
Isolation and Identification of Bacillus subtilis and Other Bacteria, Bacillus subtilis mannitol salt agar
BSMA is primarily used to isolate and identify B. subtilisfrom various sources, including food, environmental samples, and clinical specimens. It can also be used to differentiate B. subtilisfrom other closely related species, such as B. cereusand B. pumilus.
Application in Food Microbiology and Environmental Monitoring
BSMA is commonly employed in food microbiology to detect the presence of B. subtilis, which can cause food spoilage and contamination. It is also used in environmental monitoring to assess the presence of B. subtilisin soil, water, and other environmental samples.
Procedure for Using Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar
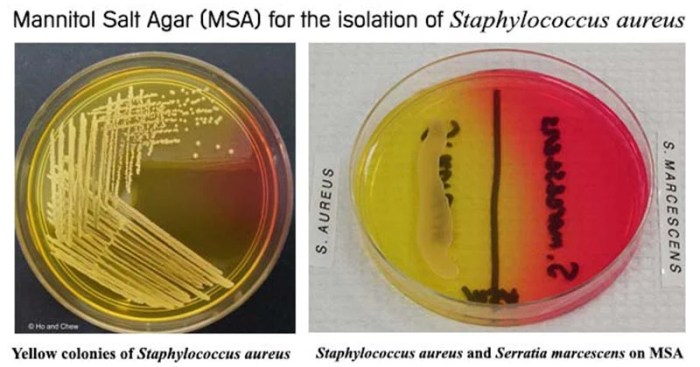
Preparation of the Agar
- Suspend 55 g of BSMA powder in 1 liter of distilled water.
- Bring to a boil while stirring to dissolve completely.
- Autoclave at 121°C for 15 minutes.
- Cool to 45-50°C before pouring into sterile petri dishes.
Sample Collection and Inoculation
- Collect samples using appropriate methods based on the source (e.g., swabbing, plating).
- Inoculate the BSMA plates by streaking the sample onto the surface.
- Incubate the plates at 37°C for 24-48 hours.
Interpretation of Results
Appearance of Bacterial Colonies
- B. subtiliscolonies typically appear as large, flat, circular, and opaque with a wrinkled or rough surface.
- They are usually pale yellow to orange in color and may have a slightly raised center.
- Other bacteria may appear as smaller, more transparent, or differently colored colonies.
Significance of Mannitol Fermentation and Salt Tolerance
- B. subtilisferments mannitol, producing yellow colonies surrounded by a yellow halo due to the acid produced.
- Its ability to tolerate high salt concentrations allows it to grow on BSMA, while many other bacteria are inhibited.
Limitations and Considerations
BSMA is a selective and differential medium, but it is not foolproof. Some strains of B. subtilismay not ferment mannitol or may be sensitive to high salt concentrations, leading to false-negative results. Additionally, other bacteria may exhibit similar growth characteristics on BSMA, requiring further biochemical or molecular testing for accurate identification.
Applications in Research and Industry
BSMA is widely used in various research areas, including food safety, biotechnology, and environmental microbiology. It is employed to study the growth, survival, and ecology of B. subtilisand related species. In industry, BSMA is used for quality control in food production and for assessing the effectiveness of sterilization and disinfection procedures.
FAQ Corner: Bacillus Subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar
What is the purpose of Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar?
Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar is specifically designed to isolate and identify Bacillus subtilis, a bacterium commonly found in soil and food products.
How does Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar work?
The agar contains mannitol, a sugar that Bacillus subtilis can ferment. Fermentation produces acids that lower the pH of the agar, causing a color change from pink to yellow.
What are the limitations of Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar?
Bacillus subtilis Mannitol Salt Agar is not suitable for identifying all Bacillus species, and some other bacteria may also grow on the agar, potentially leading to false positives.