Business intranets are secured via a comprehensive suite of security measures that encompass protocols, firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, access control, network segmentation, audits, and user education. These measures work in concert to safeguard sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of intranet resources.
By implementing robust security measures, organizations can mitigate cyber threats, enhance data protection, and maintain compliance with industry standards. This ensures the reliability, availability, and security of business intranets, empowering organizations to conduct their operations with confidence and peace of mind.
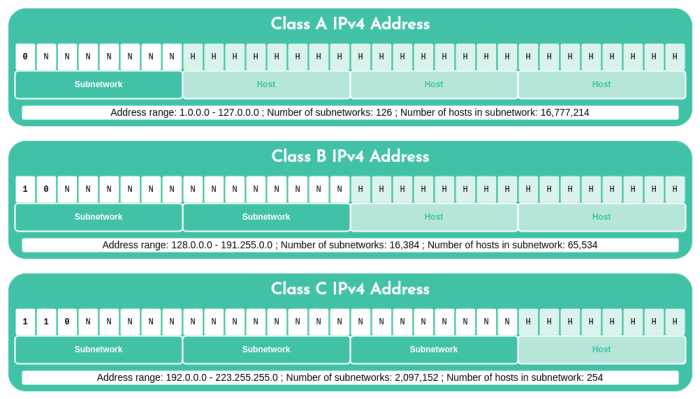
Security Protocols: Business Intranets Are Secured Via
![]()
Business intranets are secured using a combination of security protocols that provide encryption and access control mechanisms. Encryption methods, such as SSL/TLS, ensure that data transmitted over the network is protected from unauthorized access. Access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), define who can access which resources on the intranet.
Encryption Methods
- SSL/TLS: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) are cryptographic protocols that provide secure communication over a network. They encrypt data in transit, preventing eavesdropping and data tampering.
- IPsec: Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a suite of protocols that provides secure communication at the network layer. It encrypts IP packets, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of data.
Access Control Mechanisms, Business intranets are secured via
- RBAC: Role-based access control (RBAC) is a method of controlling access to resources based on the user’s role within the organization. Each role is assigned a set of permissions that define which resources the user can access.
- LDAP: Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a directory service that stores information about users, groups, and other objects. It can be used to implement access control by providing a centralized repository of user information.
Firewall Protection

Firewalls are network security devices that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. They prevent unauthorized access to the intranet by blocking traffic from untrusted sources. Firewalls can be hardware-based, software-based, or a combination of both.
Types of Firewalls
- Packet-filtering firewalls: These firewalls inspect each packet of data that passes through them and block packets that do not match predefined security rules.
- Stateful inspection firewalls: These firewalls track the state of network connections and use this information to make more informed decisions about which packets to allow or block.
- Application-layer firewalls: These firewalls inspect the application-layer data of packets and block packets that contain malicious content or that are part of known attacks.
Benefits of Firewalls
- Prevent unauthorized access to the intranet
- Protect against cyber threats, such as malware and phishing attacks
- Enforce security policies
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS)
IDPSs are security devices that monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. They can detect and prevent security breaches by identifying and blocking malicious traffic.
Types of IDPSs
- Network-based IDPSs: These IDPSs monitor network traffic for suspicious activity. They can detect and block attacks, such as denial-of-service attacks and port scans.
- Host-based IDPSs: These IDPSs monitor individual hosts for suspicious activity. They can detect and block attacks, such as malware infections and rootkits.
Benefits of IDPSs
- Detect and prevent security breaches
- Identify and block malicious traffic
- Provide early warning of security threats
Access Control and Authentication
Access control and authentication are essential security measures that prevent unauthorized access to business intranets. Access control defines who can access the intranet and what resources they can access. Authentication verifies the identity of users before granting them access.
Access Control Methods
- RBAC: Role-based access control (RBAC) is a method of controlling access to resources based on the user’s role within the organization. Each role is assigned a set of permissions that define which resources the user can access.
- LDAP: Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a directory service that stores information about users, groups, and other objects. It can be used to implement access control by providing a centralized repository of user information.
- Kerberos: Kerberos is a network authentication protocol that provides secure authentication for client-server applications. It uses a trusted third party, called a key distribution center (KDC), to issue tickets that grant users access to resources.
Authentication Mechanisms
- Password authentication: Password authentication is the most common method of authentication. Users enter a password to prove their identity.
- Multi-factor authentication: Multi-factor authentication (MFA) requires users to provide multiple forms of identification, such as a password, a security token, or a biometric identifier.
- Biometrics: Biometrics are unique physical or behavioral characteristics that can be used to identify individuals. Biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, are becoming increasingly popular.
Question Bank
What are the key security protocols used to secure business intranets?
Encryption protocols, such as SSL/TLS, are used to protect data in transit, while authentication protocols, such as LDAP and Kerberos, are used to verify user identities and control access to resources.
How do firewalls contribute to intranet security?
Firewalls act as barriers between the intranet and the external network, blocking unauthorized access and preventing the spread of malware and cyber threats.
What is the role of intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) in intranet security?
IDPS monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and can detect and prevent security breaches in real-time.