On your subnet how many ipv4 addresses were scanned – Understanding how many IPv4 addresses were scanned on your subnet is a crucial aspect of network security and IP address management. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of IP address scanning, exploring the techniques, tools, and best practices involved.
By gaining a thorough understanding of this topic, network administrators can effectively identify and mitigate potential security risks, ensuring the integrity and availability of their networks.
IP Address Scanning Overview
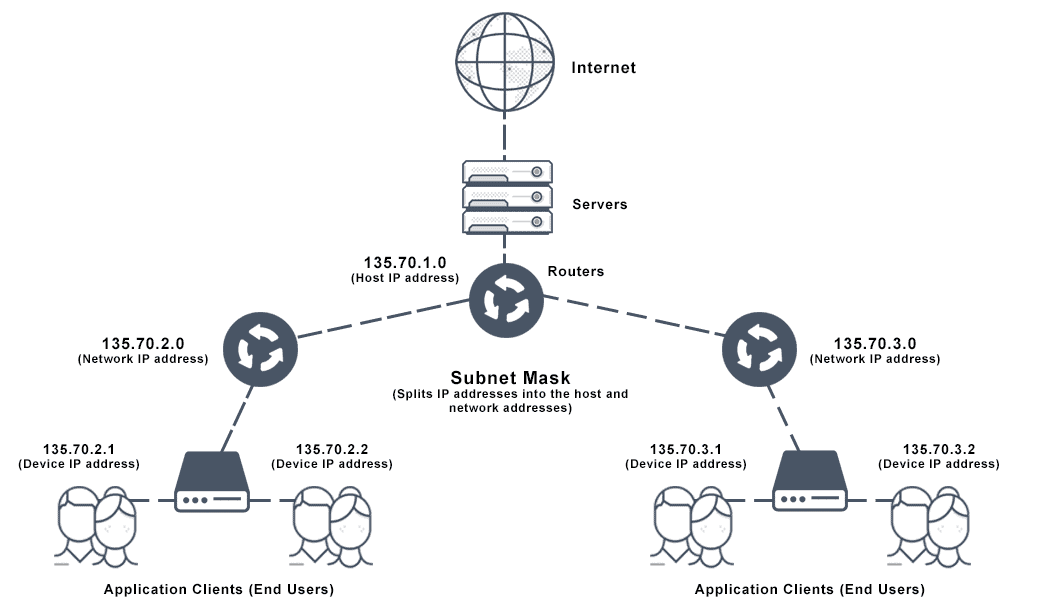
IP address scanning is a network reconnaissance technique that involves systematically probing a range of IP addresses to identify active hosts and their associated services. It is commonly used by network administrators to discover devices on their network, assess their security posture, and identify potential vulnerabilities.
The process of scanning a subnet for IPv4 addresses involves sending a series of ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets to each address in the range. If a host is active and responds to the ICMP packets, it is considered “alive” and its IP address is recorded.
Various tools and techniques can be used for IP address scanning, including:
- Nmap (Network Mapper): A versatile open-source tool that supports a wide range of scanning techniques.
- Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer that can be used to capture and analyze ICMP packets.
- Ping: A simple command-line tool that sends ICMP packets to a specified IP address.
Subnet Analysis: On Your Subnet How Many Ipv4 Addresses Were Scanned
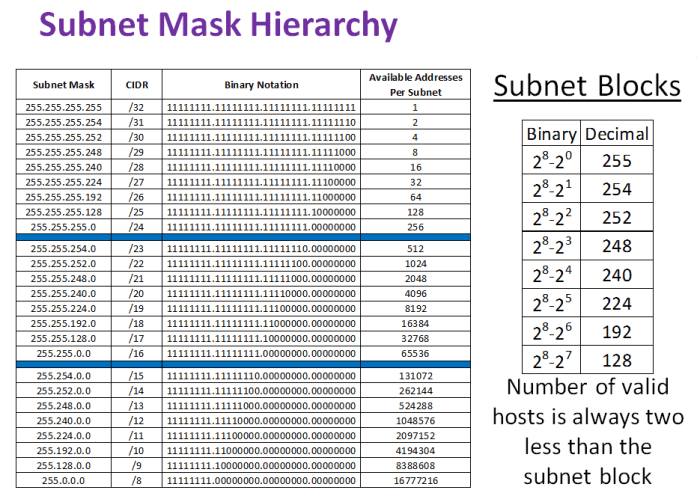
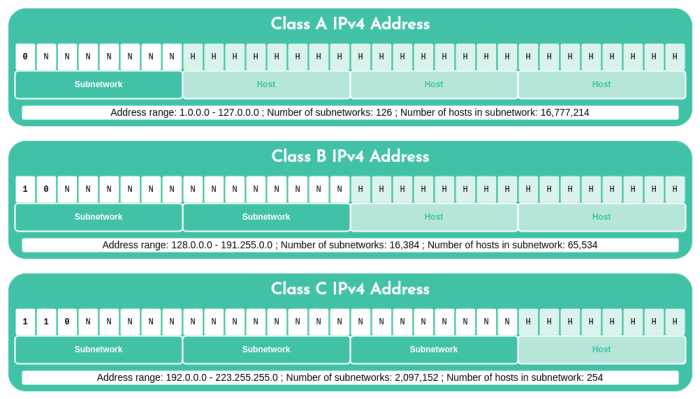
A subnet is a portion of an IP network that is assigned a unique network address and subnet mask. The subnet mask defines the number of bits in the IP address that are used to identify the subnet, while the remaining bits are used to identify the host within the subnet.
To determine the subnet mask and subnet range, you can use the following formula:
Subnet Mask = 2(32
Subnet Prefix Length)
For example, a subnet with a prefix length of 24 would have a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0, and a subnet range of 255.255.255.0 – 255.255.255.255.
The size of the subnet is determined by the subnet mask. A smaller subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0) results in a larger subnet with more hosts, while a larger subnet mask (e.g., 255.255.255.255) results in a smaller subnet with fewer hosts.
Scanning Methods
There are several methods for scanning IP addresses, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
- ICMP Ping Scan:Sends ICMP echo requests to each IP address and listens for responses. Simple and efficient, but can be blocked by firewalls.
- TCP Port Scan:Connects to each IP address on a specified port and checks for a response. More thorough than ICMP scanning, but can be slower and more intrusive.
- UDP Port Scan:Similar to TCP port scanning, but uses UDP packets instead of TCP packets. Can be useful for scanning hosts that have UDP services running.
- SYN Scan:Sends a TCP SYN packet to each IP address and checks for a SYN-ACK response. Can be used to evade firewalls that block regular TCP scans.
- ACK Scan:Sends a TCP ACK packet to each IP address and checks for a response. Can be used to identify hosts that are listening on specific ports without establishing a full connection.
The choice of scanning method depends on the specific requirements of the scan, such as the desired level of stealth, the target network’s security posture, and the available resources.
Results Interpretation
The results of an IP address scan can provide valuable information about the target network, including:
- Active Hosts:The IP addresses of all hosts that responded to the scan.
- Open Ports:The ports that are open on each active host.
- Services:The services that are running on each active host.
By analyzing the scan results, it is possible to identify potential security risks, such as open ports that are vulnerable to attack or hosts that are running outdated or vulnerable software.
Common patterns and indicators that may indicate a security risk include:
- Open ports that are known to be vulnerable to attack, such as port 21 (FTP) or port 445 (SMB).
- Hosts that are running outdated or vulnerable software, such as older versions of Windows or Apache.
- Hosts that are responding to multiple scanning methods, which may indicate that they are poorly configured or vulnerable to attack.
Best Practices
It is important to conduct IP address scans ethically and responsibly. Best practices include:
- Obtain Proper Authorization:Always obtain permission from the network owner before conducting a scan.
- Use Stealthy Techniques:Use scanning methods that are less likely to be detected by firewalls or intrusion detection systems.
- Minimize Impact:Limit the frequency and duration of scans to minimize the impact on network performance.
- Respect Privacy:Do not collect or store personal information about individuals without their consent.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your IP address scans are conducted in a responsible and ethical manner.
Expert Answers
What is IP address scanning?
IP address scanning is the process of systematically probing a range of IP addresses on a network to identify active devices and gather information about them.
What are the different methods of IP address scanning?
There are several methods of IP address scanning, including ping sweeps, port scans, and vulnerability scans, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
How do I determine the subnet mask and subnet range for my network?
The subnet mask and subnet range can be determined using the IP address and subnet mask provided by your network administrator or internet service provider.