Your team has provided face mask ppv – Face mask positive pressure ventilation (PPV) is a crucial technique used in respiratory care to support breathing in patients with respiratory distress. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of face mask PPV, covering its definition, equipment, techniques, monitoring, troubleshooting, and advanced applications.
Understanding face mask PPV is essential for healthcare professionals involved in respiratory care. This guide aims to equip readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively and safely administer face mask PPV, ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
Face Mask PPV Definition
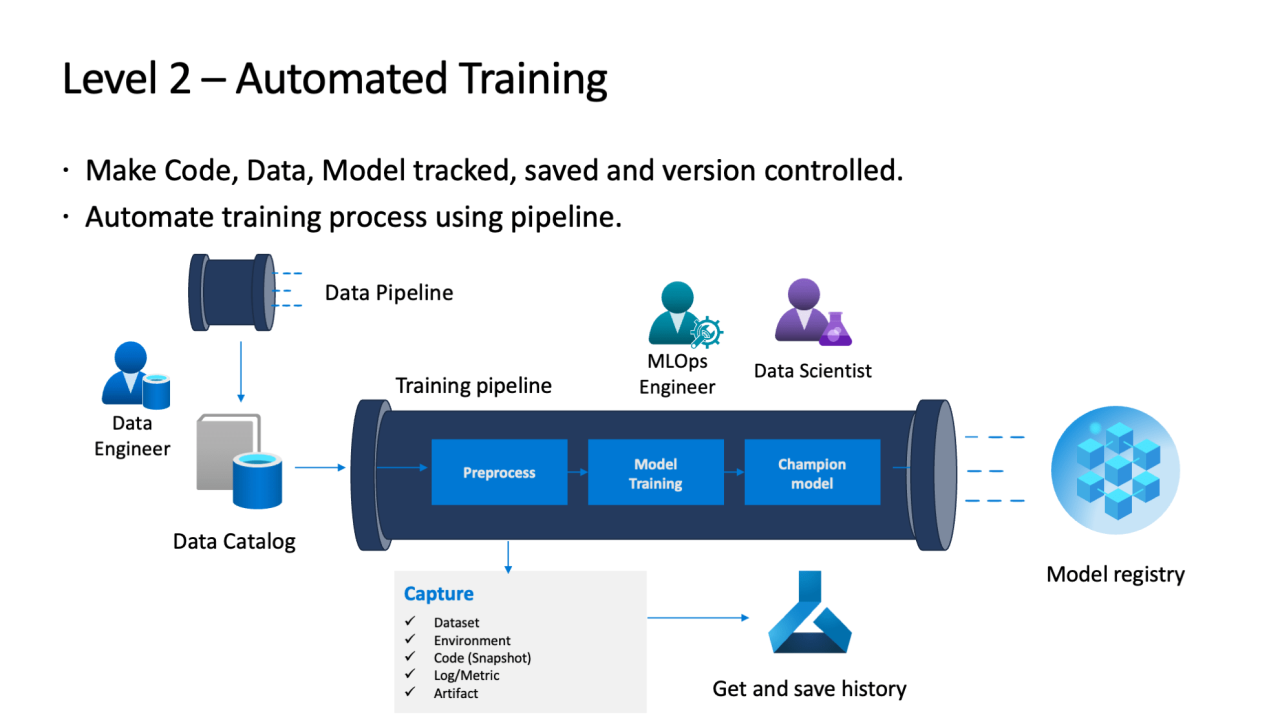
Face mask positive pressure ventilation (PPV) is a non-invasive respiratory support technique that delivers positive pressure ventilation to a patient through a face mask. It is used to assist or support breathing in patients with respiratory insufficiency or distress.
Purpose and Indications, Your team has provided face mask ppv
Face mask PPV is primarily used in emergency situations or during transport to provide immediate respiratory support to patients who are unable to breathe adequately on their own. It is indicated in conditions such as:
- Apnea or bradypnea (abnormally slow or shallow breathing)
- Hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels)
- Respiratory acidosis (increased blood acidity due to CO2 retention)
- Cardiac arrest
- Severe trauma or injuries affecting the airway or breathing
Equipment and Setup

Face mask positive pressure ventilation (PPV) requires specific equipment to effectively deliver oxygen to the patient. Understanding the components and their proper assembly is crucial for successful ventilation.
The essential equipment for face mask PPV includes:
- Face mask:A clear, disposable mask that fits snugly over the patient’s nose and mouth, creating a seal to prevent air leakage.
- Reservoir bag:A collapsible bag that stores oxygen and provides a reservoir of gas for ventilation.
- Oxygen source:A compressed oxygen cylinder or concentrator that supplies a continuous flow of oxygen.
Assembling the Equipment
To assemble the equipment for face mask PPV, follow these steps:
- Connect the oxygen source to the reservoir bag using an appropriate adapter.
- Attach the face mask to the reservoir bag via a one-way valve, ensuring a secure connection.
- Adjust the oxygen flow rate to the desired level, typically between 10-15 liters per minute.
- Verify the mask’s seal by observing chest rise and fall during ventilation.
Proper assembly and connection of the equipment are essential for effective and safe face mask PPV.
Techniques for Effective Ventilation

Delivering effective ventilation through a face mask requires a combination of proper techniques and equipment. This involves ensuring an adequate seal between the mask and the patient’s face, selecting the appropriate ventilation method, and monitoring patient response.
The most commonly used methods for delivering ventilation with a face mask are bag-valve-mask (BVM) and continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP).
Bag-Valve-Mask Ventilation
Bag-valve-mask ventilation is a manual technique that involves squeezing a self-inflating bag connected to a face mask to deliver breaths to the patient. The bag is compressed and released rhythmically to provide positive pressure ventilation. BVM ventilation is often used in emergency situations or when mechanical ventilation is not available.
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) is a non-invasive ventilation technique that delivers a constant positive pressure to the patient’s airway through a face mask. CPAP helps to keep the airway open and improve oxygenation. It is commonly used in patients with sleep apnea or respiratory distress syndrome.
Importance of Proper Mask Seal and Patient Positioning
Achieving a proper seal between the face mask and the patient’s face is crucial for effective ventilation. A poor seal can lead to air leakage and reduced ventilation efficiency. Proper patient positioning, such as elevating the head of the bed or using a chin lift, can help maintain a good mask seal and facilitate ventilation.
Monitoring and Assessment

Monitoring and assessment are essential during face mask PPV to ensure adequate ventilation and prevent complications.
The following parameters should be monitored:
- Vital signs:Heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate
- Oxygen saturation:Pulse oximetry
- Respiratory rate:Measured by observing chest rise and fall
Signs and symptoms of inadequate ventilation include:
- Cyanosis
- Tachycardia
- Bradypnea
- Hypotension
li>Altered level of consciousness
If signs of inadequate ventilation are observed, the following adjustments should be made:
- Increase the ventilation rate
- Increase the tidal volume
- Improve the airway seal
- Administer supplemental oxygen
Troubleshooting Common Problems
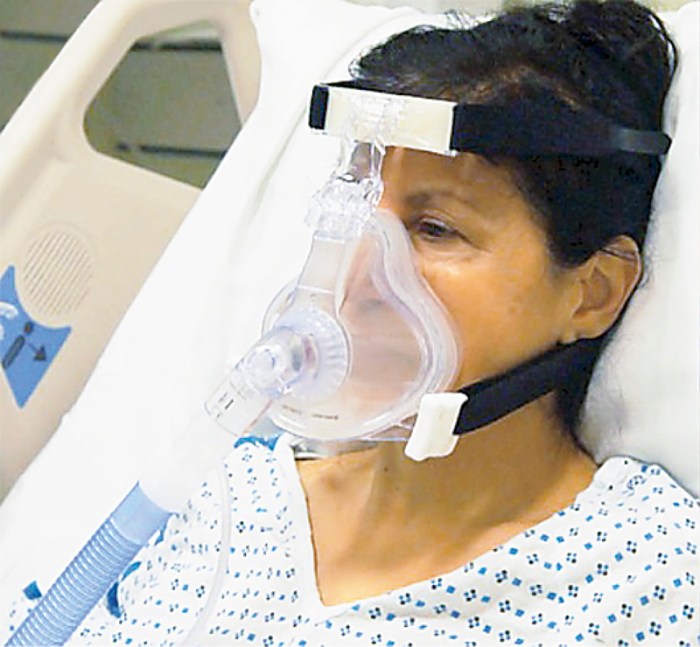
Face mask PPV is a generally safe and effective technique for providing ventilation, but some common problems can arise during its use. Identifying and addressing these problems promptly is essential to ensure adequate oxygen delivery and patient safety.
Mask Leaks
Mask leaks occur when air escapes around the edges of the face mask, resulting in inadequate ventilation. This can be caused by an improper mask fit, facial hair, or a patient’s movement. To troubleshoot mask leaks:
- Check the mask fit and ensure it is snugly and securely positioned on the patient’s face.
- Remove any facial hair that may interfere with the mask seal.
- Use a different mask size or type if the current one is not providing a good fit.
- Reposition the patient’s head and neck to minimize movement that could cause leaks.
Patient Resistance
Patient resistance occurs when the patient actively or passively resists ventilation. This can be caused by anxiety, pain, or airway obstruction. To troubleshoot patient resistance:
- Reassure and calm the patient to reduce anxiety.
- Administer pain medication if necessary.
- Check for any airway obstructions and clear them if possible.
- Use a different mask type or size that may be more comfortable for the patient.
- Consider using a bite guard to prevent the patient from biting down on the airway.
Inadequate Oxygen Delivery
Inadequate oxygen delivery can occur due to insufficient oxygen flow, airway obstruction, or mask leaks. To troubleshoot inadequate oxygen delivery:
- Check the oxygen flow rate and adjust it as necessary.
- Inspect the airway for any obstructions and remove them.
- Check the mask fit and ensure there are no leaks.
- Consider using a different mask type or size that may provide better oxygen delivery.
- Monitor the patient’s oxygen saturation levels and adjust the ventilation parameters as needed.
Advanced Techniques

Advanced techniques for face mask PPV include two-person ventilation and non-invasive positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV). These techniques offer enhanced ventilation and oxygenation, particularly in challenging situations or when prolonged ventilation is required.
Two-Person Ventilation
Two-person ventilation involves the coordination of two providers, one managing the mask and the other delivering compressions. This technique provides more effective ventilation, especially in obese patients or those with airway resistance.
Benefits of two-person ventilation include:
- Increased tidal volumes and improved oxygenation
- Reduced risk of gastric insufflation
- Enhanced airway patency and reduced resistance
Non-Invasive Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV)
NIPPV is a non-invasive method of providing positive pressure ventilation through a face mask or nasal prongs. It supports spontaneous breathing and improves gas exchange.
Indications for NIPPV include:
- Acute respiratory failure
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Benefits of NIPPV include:
- Reduced intubation rates
- Improved oxygenation and ventilation
- Enhanced patient comfort and cooperation
Top FAQs: Your Team Has Provided Face Mask Ppv
What is the purpose of face mask PPV?
Face mask PPV provides positive pressure ventilation to patients with respiratory distress, assisting in breathing and improving oxygenation.
What are the indications for using face mask PPV?
Face mask PPV is indicated in situations where patients require respiratory support, such as respiratory failure, apnea, or inadequate spontaneous breathing.
What equipment is necessary for face mask PPV?
Face mask PPV requires a face mask, reservoir bag, oxygen source, and connecting tubing.