Why did francis townsend oppose the new deal – Francis Townsend’s opposition to the New Deal, a pivotal moment in American history, stemmed from his profound belief that it failed to adequately address the rampant unemployment and poverty plaguing the nation during the Great Depression. Townsend, a renowned physician and political activist, vehemently advocated for a universal pension plan as a more effective solution to the economic crisis.
Townsend’s criticism of the New Deal extended beyond its perceived inadequacy in tackling unemployment. He expressed concerns about its potential inflationary effects, its favoritism towards wealthy individuals and corporations over the working class, and its perceived overreach in regulating industry and labor.
Francis Townsend’s Opposition to the New Deal: Core Reasons

Francis Townsend, a physician and social activist, emerged as a staunch critic of President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal policies. He believed that the New Deal failed to adequately address the root causes of unemployment and poverty prevalent during the Great Depression.
Townsend’s primary objection was the New Deal’s reliance on temporary relief measures, such as the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) and the Works Progress Administration (WPA), which he argued were insufficient to provide long-term economic security for the unemployed.
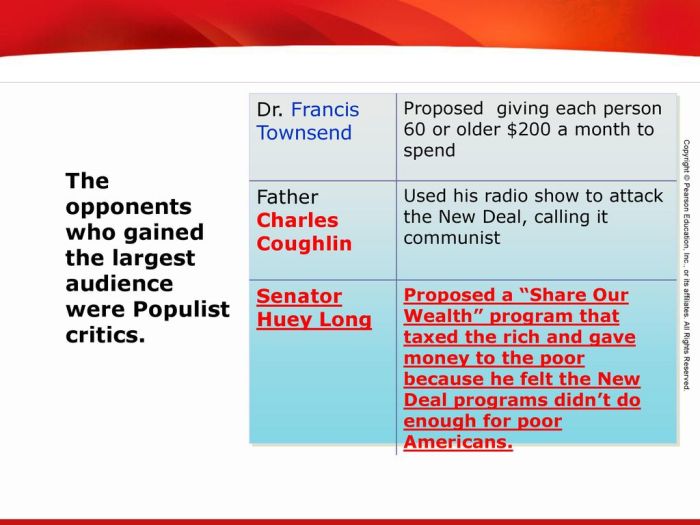
Instead, Townsend advocated for a universal pension plan that would provide every American over the age of 60 with a monthly payment of $200. He believed that this plan would stimulate economic activity by increasing consumer spending and reducing the burden on the government to provide relief.
Townsend also criticized the New Deal’s job creation programs, arguing that they were inefficient and wasteful. He pointed to the fact that many of the jobs created through these programs were low-paying and did not provide permanent employment.
Townsend’s Concerns Regarding New Deal Policies
In addition to his opposition to the New Deal’s economic policies, Townsend also raised concerns about its potential inflationary effects.
Townsend believed that the New Deal’s emphasis on deficit spending would lead to a rapid increase in the money supply, which in turn would drive up prices and erode the value of savings.
Townsend also argued that the New Deal favored wealthy individuals and corporations over the working class. He criticized the New Deal’s tax policies, which he believed shifted the tax burden away from the wealthy and onto the poor.
Additionally, Townsend objected to the New Deal’s regulation of industry and labor. He believed that these regulations would stifle economic growth and lead to higher unemployment.
Townsend’s Political Strategies and Impact
Townsend’s opposition to the New Deal gained significant traction through the Townsend Movement, which he founded in 1934. The movement quickly grew in popularity, with millions of Americans signing petitions and attending rallies in support of Townsend’s pension plan.
The Townsend Movement had a significant influence on the New Deal. It forced the Roosevelt administration to address the issue of unemployment and poverty more directly.
While Townsend’s pension plan was never adopted, the movement helped lay the groundwork for the Social Security Act of 1935, which established a national pension system for the elderly.
The Townsend Movement declined in the late 1930s as the economy began to recover. However, Townsend’s ideas continued to influence American politics, inspiring subsequent social welfare programs.
Townsend’s Legacy and Historical Significance

Francis Townsend’s ideas have had a lasting impact on social security and welfare programs in the United States. His advocacy for a universal pension plan helped shape the development of the American welfare state.
Townsend’s ideas remain relevant to contemporary debates about poverty and inequality. His emphasis on providing economic security for all Americans, regardless of age or employment status, continues to resonate with many.
Townsend’s legacy as a social activist and advocate for the poor and unemployed is undeniable. His ideas have helped to shape the social safety net in the United States and continue to inspire discussions about how to address poverty and inequality in the 21st century.
Quick FAQs: Why Did Francis Townsend Oppose The New Deal
What were Townsend’s primary objections to the New Deal?
Townsend believed that the New Deal did not adequately address unemployment and poverty, favored the wealthy, and overreached in regulating industry and labor.
How did Townsend propose to address the economic crisis?
Townsend advocated for a universal pension plan that would provide a monthly payment to all Americans over the age of 60.
What was the impact of Townsend’s ideas on American social welfare policy?
Townsend’s advocacy for a universal pension plan laid the groundwork for the establishment of Social Security, and his critique of the New Deal’s perceived shortcomings contributed to the development of a more comprehensive and robust welfare state.