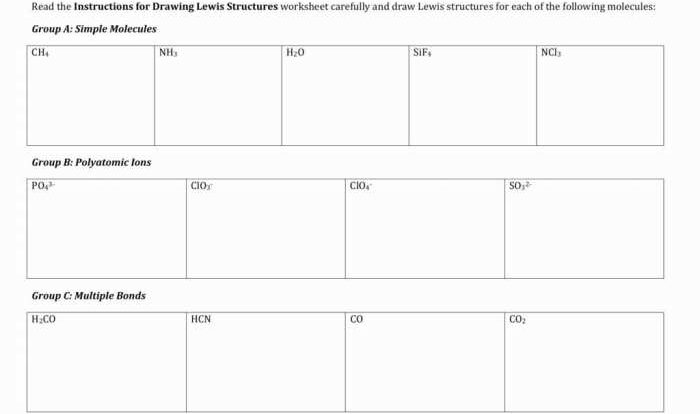
Which equation represents an exothermic reaction at 298 K? This question delves into the fascinating realm of thermodynamics, where we explore the intricacies of energy transfer in chemical reactions. Exothermic reactions, characterized by the release of heat, play a crucial role in various scientific and industrial applications.
In this analysis, we will delve into the concept of exothermic reactions, investigate the role of enthalpy in determining their spontaneity, and uncover the practical implications of these reactions in our everyday lives.
Exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat. This energy release is accompanied by a decrease in the enthalpy of the system, making the reaction exothermic. Enthalpy, denoted by the symbol H, represents the total thermal energy of a system, including its internal energy and the work done by or on the system.
In exothermic reactions, the decrease in enthalpy indicates that the products of the reaction have less energy than the reactants, and the excess energy is released as heat.
1. Introduction to Exothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions are chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat. They are characterized by a negative change in enthalpy, indicating that the products of the reaction have less energy than the reactants. Exothermic reactions are common in many natural and industrial processes.
Some common examples of exothermic reactions include combustion, the reaction of metals with acids, and the neutralization of strong acids and bases.
2. Enthalpy and Exothermic Reactions
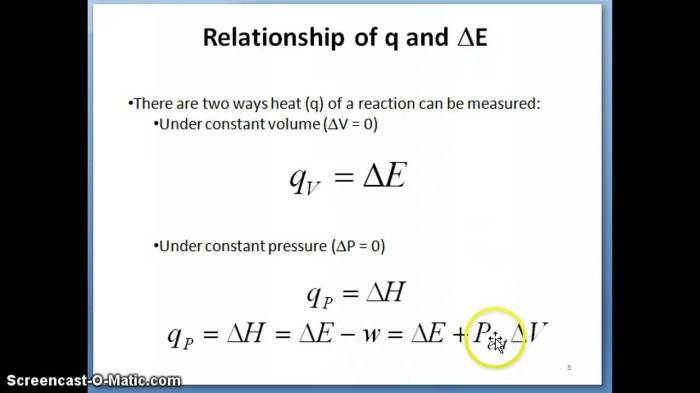
Enthalpy is a thermodynamic property that measures the total energy of a system. In chemical reactions, the change in enthalpy (ΔH) is the difference in enthalpy between the products and the reactants.
For exothermic reactions, ΔH is negative because the products have less energy than the reactants. This means that energy is released during the reaction.
3. Identifying Exothermic Reactions at 298 K

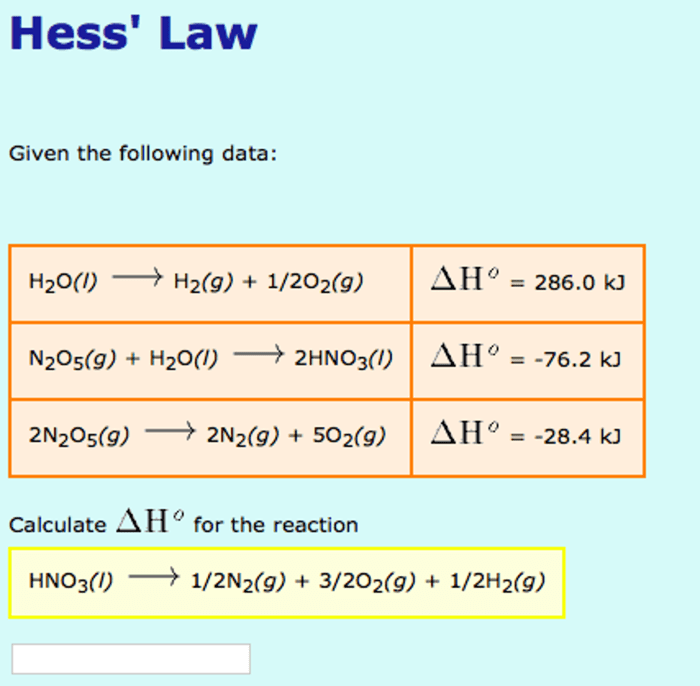
The standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH fo) is a measure of the enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states.
Using standard enthalpy of formation values, we can calculate the enthalpy change of a reaction using the following equation:
ΔH = ΣΔHfo(products)
ΣΔHfo(reactants)
If ΔH is negative, the reaction is exothermic at 298 K.
4. Applications of Exothermic Reactions
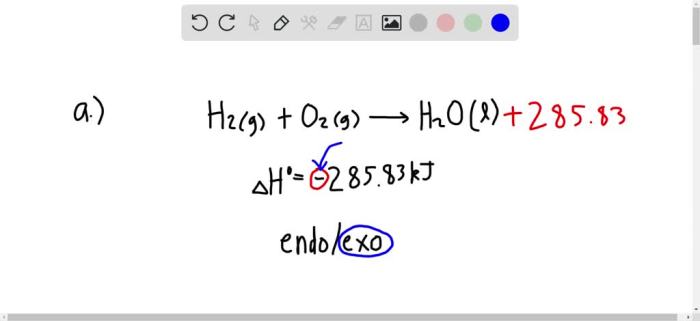
Exothermic reactions have many practical applications in various fields, including:
- Energy production:Exothermic reactions are used to generate electricity in power plants.
- Industrial processes:Exothermic reactions are used in the production of many industrial chemicals, such as steel and cement.
5. Examples of Exothermic Reactions: Which Equation Represents An Exothermic Reaction At 298 K
| Reaction Equation | Enthalpy Change (kJ/mol) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O | -572 | Combustion of hydrogen |
| Mg + 2HCl → MgCl2 + H2 | -459 | Reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid |
| NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O | -56 | Neutralization of sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid |
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of exothermic reactions?
Exothermic reactions play a vital role in various fields, including energy production, industrial processes, and everyday applications. They are utilized in power plants to generate electricity, in manufacturing processes to create materials, and in everyday products such as hand warmers and heat packs.
How can we determine if a reaction is exothermic or endothermic?
The enthalpy change of a reaction, denoted by ΔH, determines whether it is exothermic or endothermic. If ΔH is negative, the reaction is exothermic, indicating the release of heat. Conversely, if ΔH is positive, the reaction is endothermic, indicating the absorption of heat.
What are some examples of exothermic reactions?
Common examples of exothermic reactions include combustion reactions, such as burning wood or gasoline, which release significant amounts of heat. Other examples include the neutralization reaction between an acid and a base, the precipitation reaction between two ionic solutions, and the hydration reaction of anhydrous compounds.