Neck cat lymph nodes diagram – Embark on a journey into the intricacies of neck cat lymph nodes, where we unravel the secrets of these crucial immune system components. Discover their anatomy, function, and how to identify abnormalities, empowering you with knowledge to safeguard your feline companion’s well-being.
Delving into the classification and types of lymph nodes, we explore their diverse roles within the neck. Learn how to palpate and examine these nodes, recognizing normal characteristics and detecting signs of potential health concerns.
Neck Cat Lymph Nodes
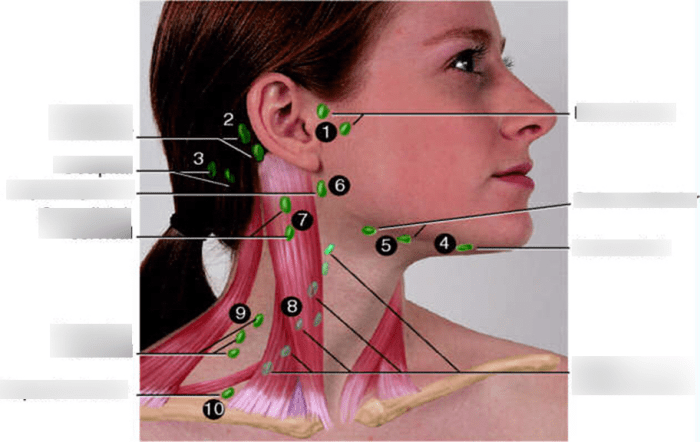
The neck of cats, like other animals, contains several lymph nodes that play a crucial role in the immune system. These lymph nodes are strategically located to filter and monitor lymph fluid, which carries immune cells and other substances from tissues throughout the body.
Anatomy and Location
The lymph nodes in the neck of cats are organized into groups or chains, each with a specific drainage area. The main groups include:
-
-*Mandibular Lymph Nodes
Located under the jawbone, these nodes drain lymph from the head, face, and mouth.
-*Retropharyngeal Lymph Nodes
Situated behind the pharynx (throat), these nodes receive lymph from the nasal cavity, tonsils, and pharynx.
-*Cervical Lymph Nodes
Found along the sides of the neck, these nodes drain lymph from the skin, muscles, and other tissues in the neck.
Function in the Immune System
Lymph nodes are essential components of the immune system, performing several critical functions:
-
-*Filtration
Lymph nodes filter lymph fluid, removing bacteria, viruses, and other foreign particles.
-*Immune Cell Production
They produce immune cells, such as lymphocytes, which are responsible for recognizing and attacking pathogens.
-*Antigen Presentation
Lymph nodes present antigens (foreign substances) to immune cells, triggering an immune response.
-*Memory Cell Storage
Lymph nodes store memory cells, which provide long-term immunity to previously encountered pathogens.
Classification and Types
Neck lymph nodes in cats are classified into several groups based on their location and function.
There are three main types of lymph nodes found in the neck of cats:
Superficial Lymph Nodes
- Located just beneath the skin and fascia
- Receive lymph from the skin, superficial muscles, and other structures in the neck
- Include the mandibular, parotid, and superficial cervical lymph nodes
Deep Lymph Nodes, Neck cat lymph nodes diagram
- Located deep within the neck, associated with major blood vessels and nerves
- Receive lymph from deeper structures, such as the larynx, pharynx, and esophagus
- Include the retropharyngeal, deep cervical, and cranial mediastinal lymph nodes
Accessory Lymph Nodes
- Not consistently present in all cats
- Located along the course of the jugular vein
- Receive lymph from the head and neck
Palpation and Examination
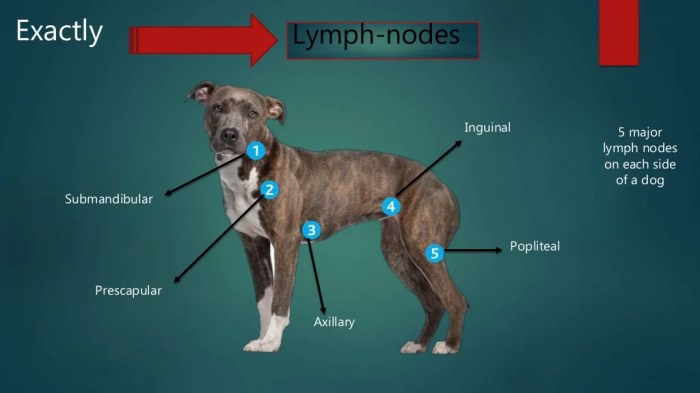
Palpation is a crucial technique for examining lymph nodes in the neck of cats. By gently feeling the nodes, veterinarians can assess their size, shape, and consistency, providing valuable insights into their health.
Normal Lymph Nodes
Normal lymph nodes in cats are typically small, round or oval, and firm to the touch. They are usually not visible or palpable unless they become enlarged due to infection or other conditions.
Abnormal Lymph Nodes
Abnormal lymph nodes may exhibit various signs and symptoms, including:
- Enlargement: Enlarged lymph nodes may indicate infection, inflammation, or other underlying conditions.
- Tenderness: Painful or tender lymph nodes can be a sign of infection or inflammation.
- Matting: Lymph nodes that are matted together or fixed to surrounding tissues may indicate a more severe condition, such as cancer.
- Discharge: Lymph nodes that discharge pus or other fluids may be infected or inflamed.
Diagnostic Imaging: Neck Cat Lymph Nodes Diagram
Diagnostic imaging plays a crucial role in evaluating neck lymph nodes in cats, providing valuable insights into their size, shape, and internal architecture. Various imaging modalities are employed to assess these lymph nodes, including ultrasound and radiography.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to generate real-time images of internal structures. In the context of neck lymph node evaluation, ultrasound offers several advantages:
- Visualization:Ultrasound allows for the visualization of lymph nodes, assessing their size, shape, and echogenicity (the brightness of the image).
- Internal architecture:Ultrasound can reveal the internal architecture of lymph nodes, including the presence of any abnormal structures, such as cysts or masses.
- Blood flow:Ultrasound can assess blood flow within lymph nodes using Doppler imaging, providing information about their vascularity.
Radiography
Radiography, also known as X-ray imaging, is another imaging modality used to evaluate neck lymph nodes. While not as detailed as ultrasound, radiography can provide valuable information:
- Lymph node size and shape:Radiography can reveal the size and shape of lymph nodes, although it may not provide as much detail as ultrasound.
- Calcification:Radiography can detect the presence of calcification within lymph nodes, which may indicate inflammation or infection.
- Mediastinal involvement:Radiography can assess the involvement of mediastinal lymph nodes, which are located in the chest cavity.
Biopsy and Histopathology
Lymph node biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves removing a small sample of tissue from a lymph node for examination under a microscope. This procedure is essential for diagnosing and classifying lymph node disorders in cats.
Histopathology
Histopathology is the microscopic examination of tissue samples to identify abnormalities in cell structure and organization. In the context of lymph node disorders, histopathology helps determine the type of disorder (e.g., reactive hyperplasia, lymphoma, metastasis) and assess the severity of the condition.
Understanding the neck cat lymph nodes diagram can provide valuable insights into feline anatomy. If you’re interested in exploring electrical concepts, consider checking out r s t electrical meaning for a deeper understanding. Returning to the lymph nodes diagram, it’s essential to recognize the crucial role they play in the feline immune system.
Differential Diagnoses
When evaluating enlarged or abnormal lymph nodes in the neck of cats, it is important to consider a differential diagnosis list to determine the underlying cause. Lymphadenopathy, or the enlargement of lymph nodes, can result from various conditions, including:
Infectious Causes
- Bacterial infections (e.g., abscesses, cellulitis)
- Viral infections (e.g., feline leukemia virus, feline immunodeficiency virus)
- Fungal infections (e.g., cryptococcosis)
- Parasitic infections (e.g., toxoplasmosis)
Immune-Mediated Causes
- Lymphoma
- Leukemia
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
Neoplastic Causes
- Metastatic cancer
- Primary lymph node tumors
Other Causes
- Trauma
- Inflammation (e.g., due to allergies, dental disease)
- Idiopathic (unknown cause)
Clinical Management
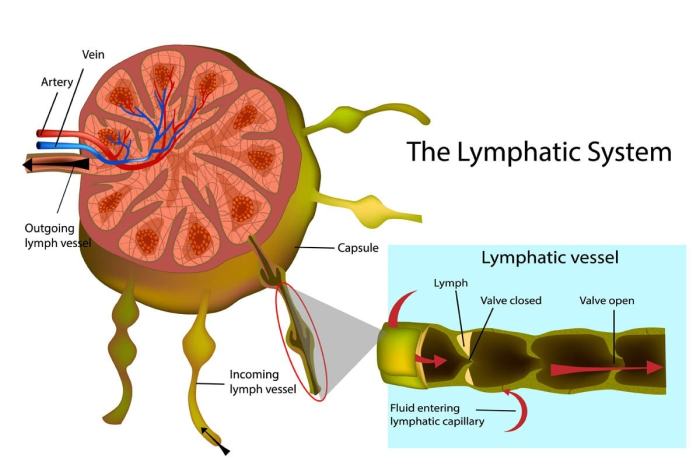
Clinical management of cats with neck lymph node disorders involves a comprehensive approach that includes diagnostic testing, treatment, and monitoring. The principles of clinical management are to determine the underlying cause of lymphadenopathy, address any underlying medical conditions, and provide supportive care as needed.
Treatment options for different types of lymphadenopathy vary depending on the underlying cause. For example, bacterial infections may require antibiotic therapy, while neoplastic conditions may require surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy. In cases of lymphadenopathy due to systemic diseases, such as immune-mediated disorders or metabolic diseases, treatment is directed at managing the underlying condition.
Supportive Care
Supportive care measures are an important aspect of clinical management for cats with neck lymph node disorders. These measures may include:
- Providing a comfortable and stress-free environment
- Administering pain medication if necessary
- Providing nutritional support, such as a high-calorie diet or appetite stimulants
- Monitoring for signs of infection or other complications
Prognosis and Prevention
The prognosis for cats with neck lymph node disorders depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. If the underlying cause is treatable, such as an infection or inflammation, the prognosis is generally good.
However, if the underlying cause is more serious, such as cancer, the prognosis may be more guarded. In some cases, neck lymph node disorders can be fatal.
Prevention
There are no specific measures that can be taken to prevent lymphadenopathy in cats. However, keeping your cat up-to-date on vaccinations and regular veterinary checkups can help to identify and treat any underlying medical conditions that could lead to lymphadenopathy.
FAQ Corner
What is the function of lymph nodes in cats?
Lymph nodes are vital components of the immune system, acting as filters that trap and destroy harmful substances, including bacteria, viruses, and cancer cells.
How can I tell if my cat’s lymph nodes are enlarged?
Enlarged lymph nodes may be palpable as small, firm swellings under the skin. However, it’s important to note that some lymph nodes are normally palpable in healthy cats.
What causes lymphadenopathy in cats?
Lymphadenopathy can result from various causes, including infections, inflammation, cancer, and immune system disorders. Proper diagnosis requires veterinary evaluation.